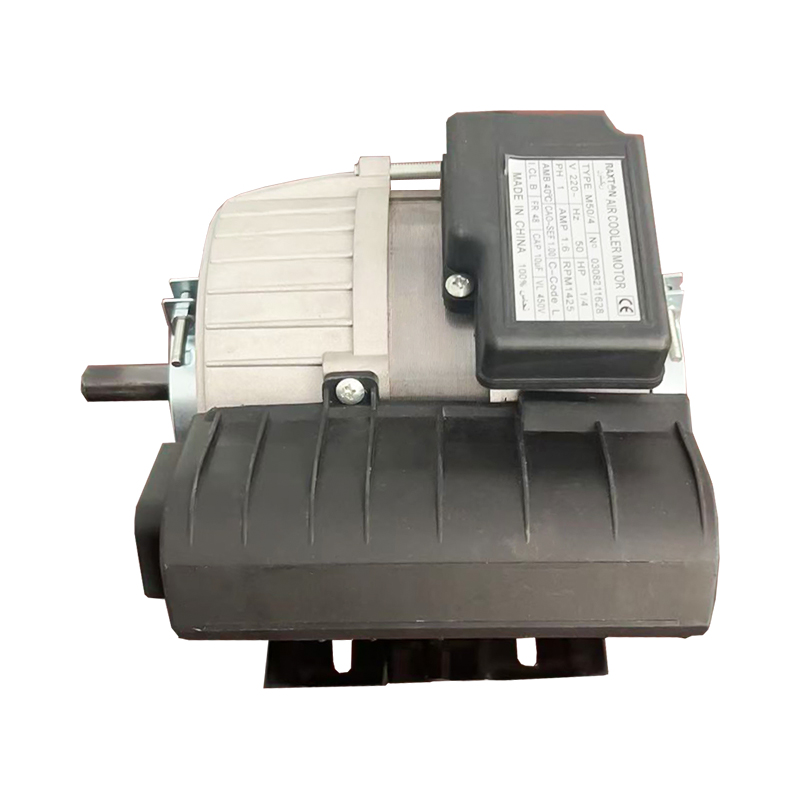
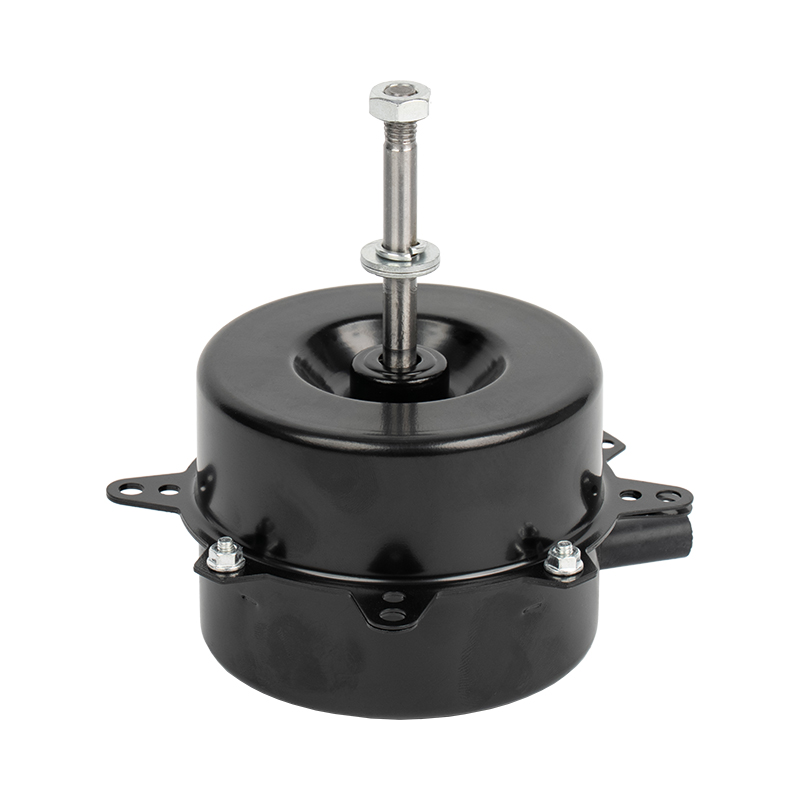
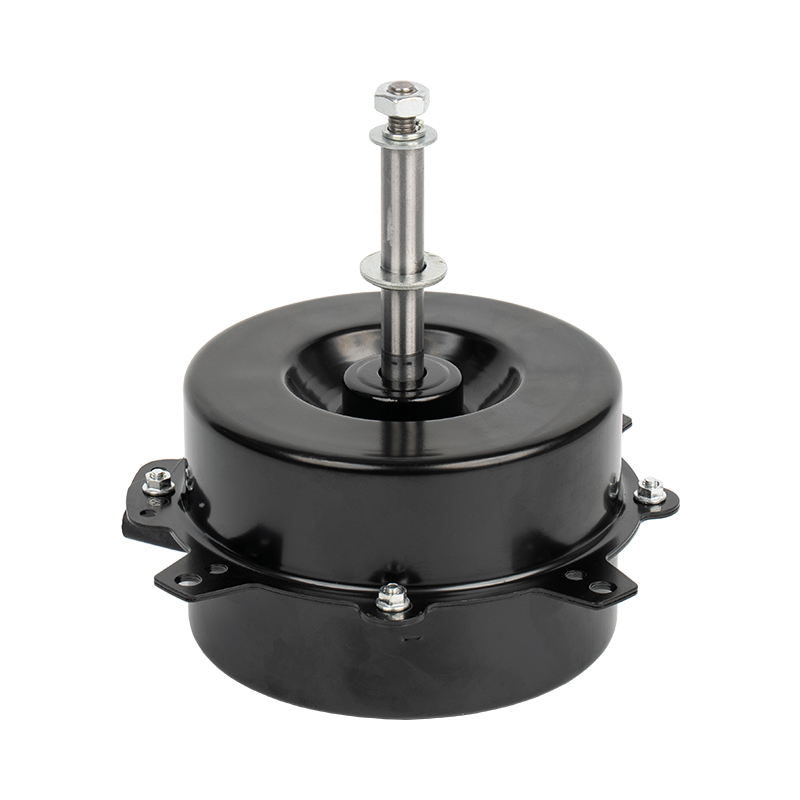
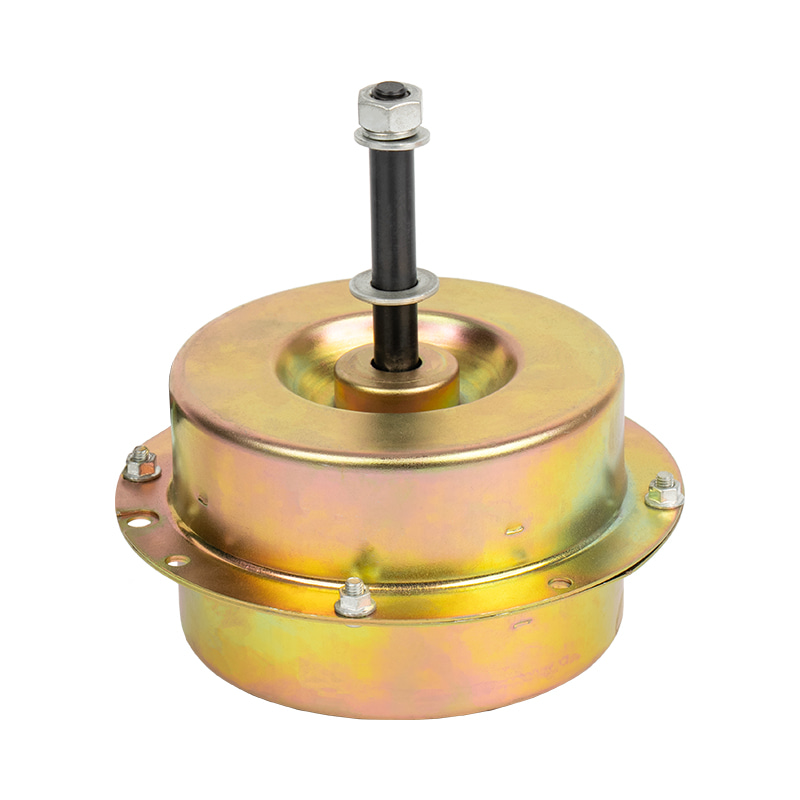
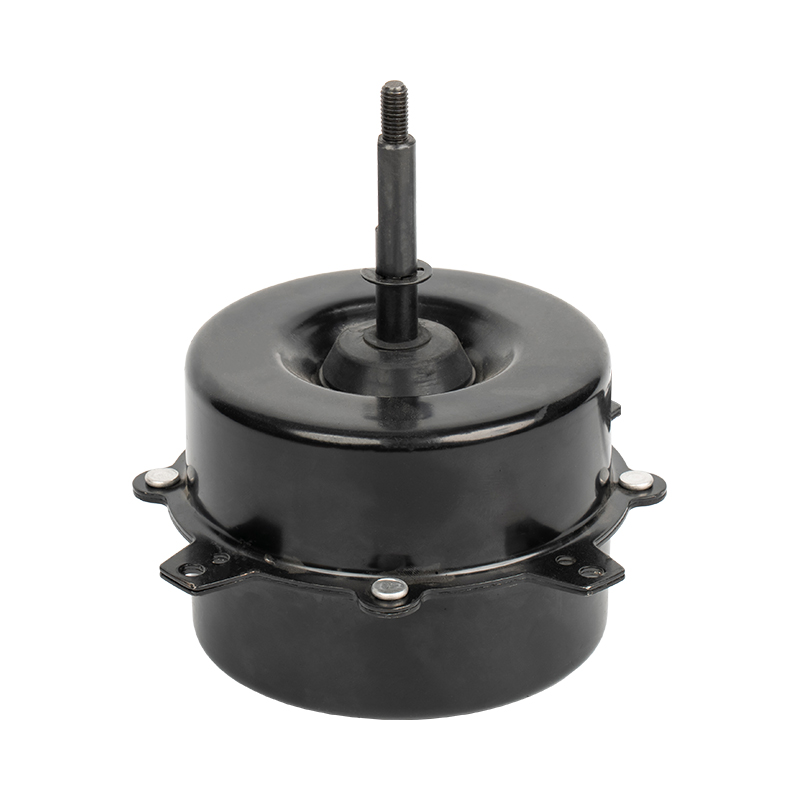
1. High - efficiency variable - frequency drive
The Air Cooler Motor uses variable - frequency technology, enabling stepless speed regulation over a wide range. In contrast, traditional AC fan motors can only switch between fixed gears. The variable - frequency motor uses electronic commutation and position sensors to control the rotor speed in real - time. It can maintain sufficient heat dissipation at low speeds and provide strong air volume at high speeds, thus significantly reducing energy consumption.
2. Independent cooling system
To ensure effective heat dissipation even at low speeds, the Air Cooler Motor uses an independent cooling fan instead of the traditional design co - axial with the rotor. This structure avoids the risk of insufficient heat dissipation due to a decrease in speed and improves long - term reliability.
3. Brushless permanent - magnet structure
Most Air Cooler Motors use a brushless permanent - magnet rotor, eliminating carbon brushes and commutators, resulting in lower noise and longer service life. Ordinary fan motors mostly have a brushed structure, and their service life is limited by carbon - brush wear, and the noise is relatively high.
4. Intelligent air - volume adjustment
Through built - in temperature and humidity sensors, the Air Cooler Motor can automatically adjust the air volume according to actual environmental needs, achieving the best cooling effect and maximizing energy utilization. Ordinary fans can only be manually adjusted in speed, making it difficult to achieve precise control.
How to determine if the Air Cooler Motor is malfunctioning?
1. The four - step method of listening, looking, and touching
Listen: Abnormal noises (such as buzzing or friction sounds) often indicate bearing wear or rotor imbalance.
Look: Check if there are signs of over - heating discoloration, oil stains, or corrosion on the motor housing.
Touch: If the temperature feels abnormally high during operation, it indicates that the cooling system may have failed.
Smell: If there is a burning smell, it may be due to a short - circuit in the winding or insulation aging.
2. Electrical parameter detection
Use a multimeter to measure the motor's resistance value, insulation resistance, and starting current. If the resistance is abnormally low or the insulation resistance is below 1 MΩ, further investigation for internal short - circuits is required.
3. Comparison of operating characteristics
Compare the current speed, air volume, and power with the factory specification sheet. If the air volume decreases by more than 15% or the power increases abnormally at the same voltage, it indicates that the motor may have reduced efficiency or internal mechanical jamming.
4. Fault codes and self - check function
Modern Air Cooler Motors are equipped with intelligent controllers that can output fault codes on the display panel. Common codes include "E - 01" (power supply abnormality) and "E - 02" (temperature sensor failure). Users can refer to the instruction manual to quickly locate the problem.


 English
English عربى
عربى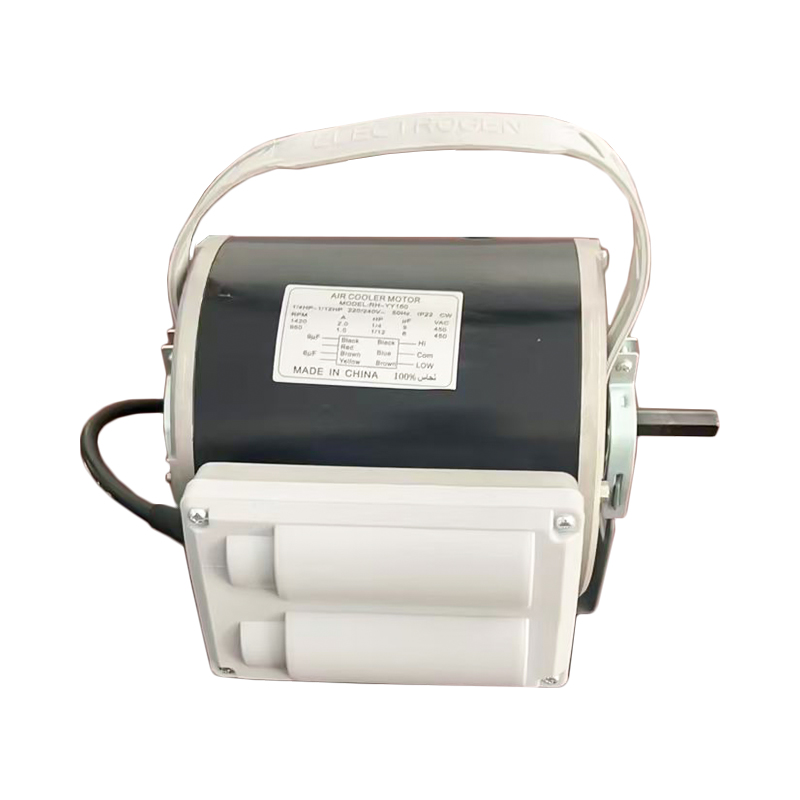













 Home
Home  Tel.: +86-13819807486
Tel.: +86-13819807486 Whatsapp:+86 13819807486
Whatsapp:+86 13819807486 E-mail:
E-mail: