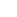
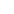
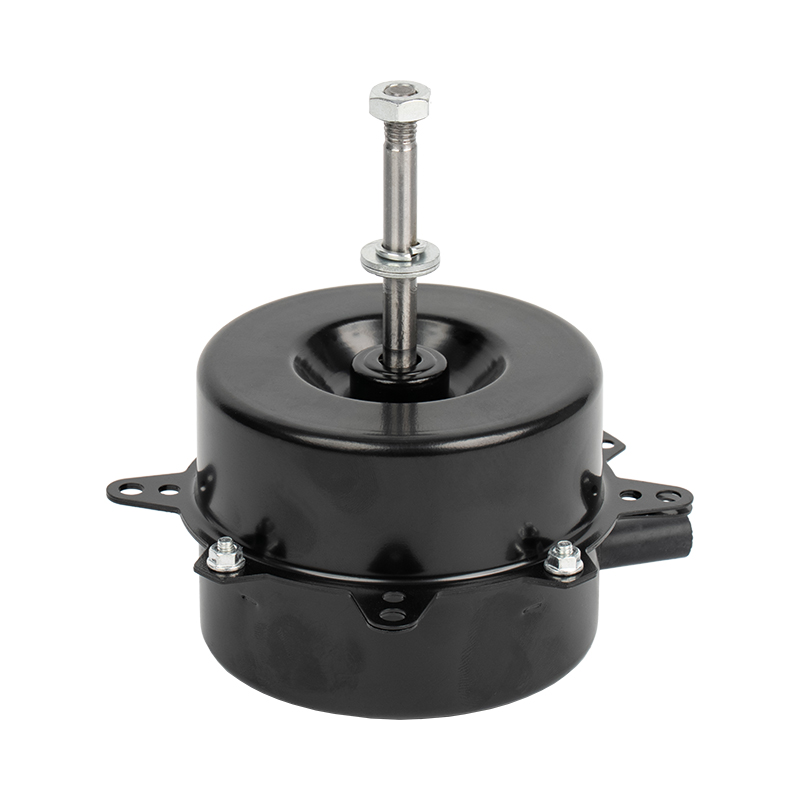
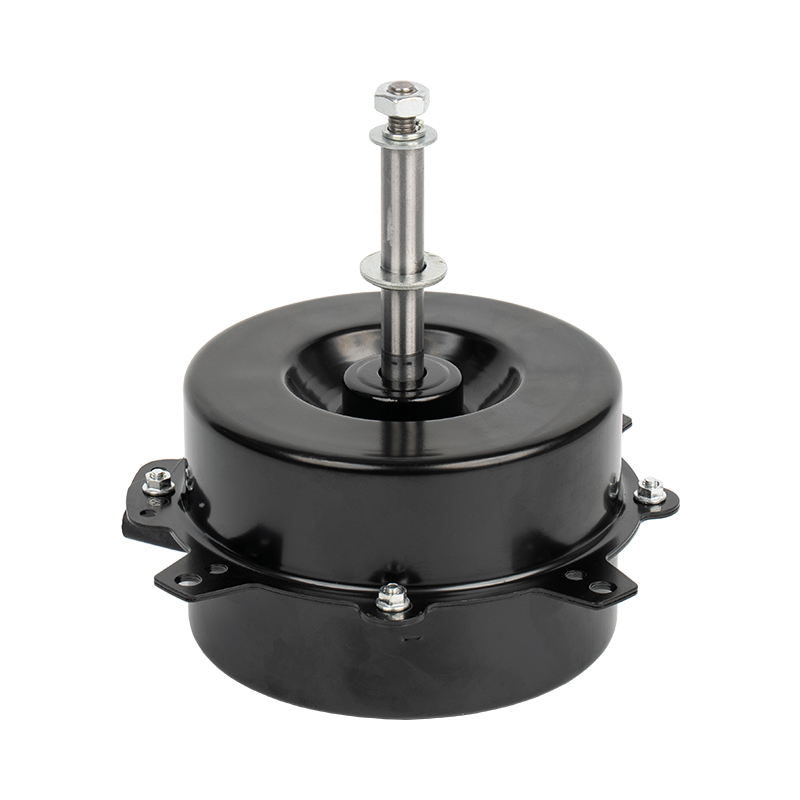
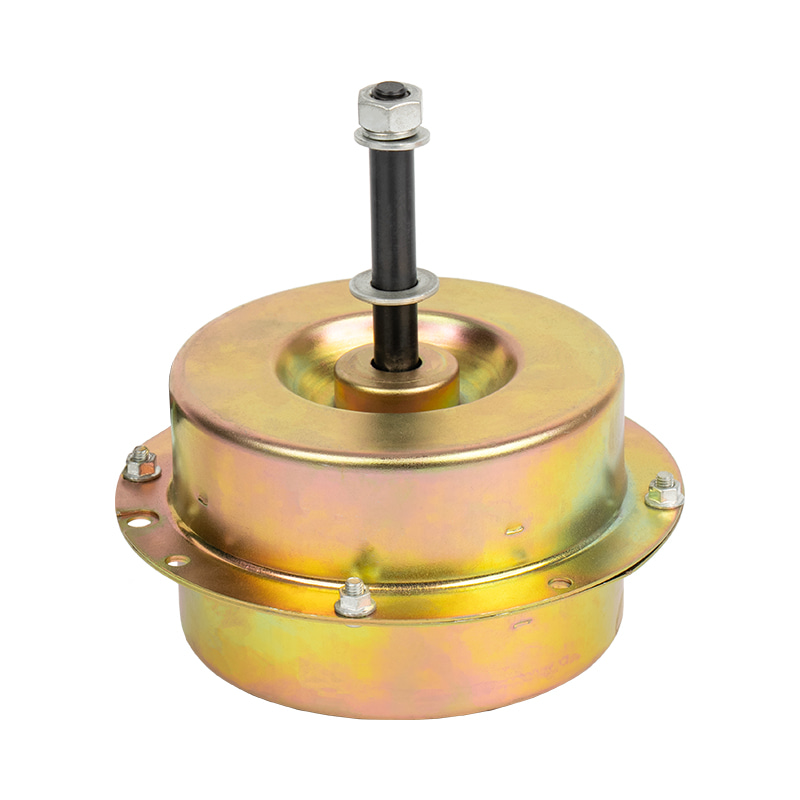
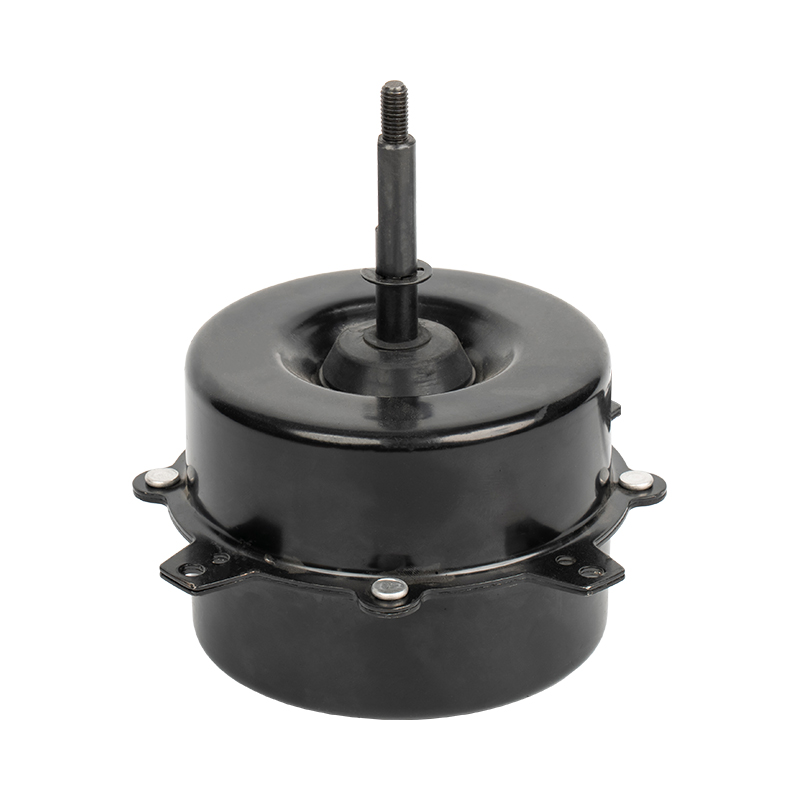
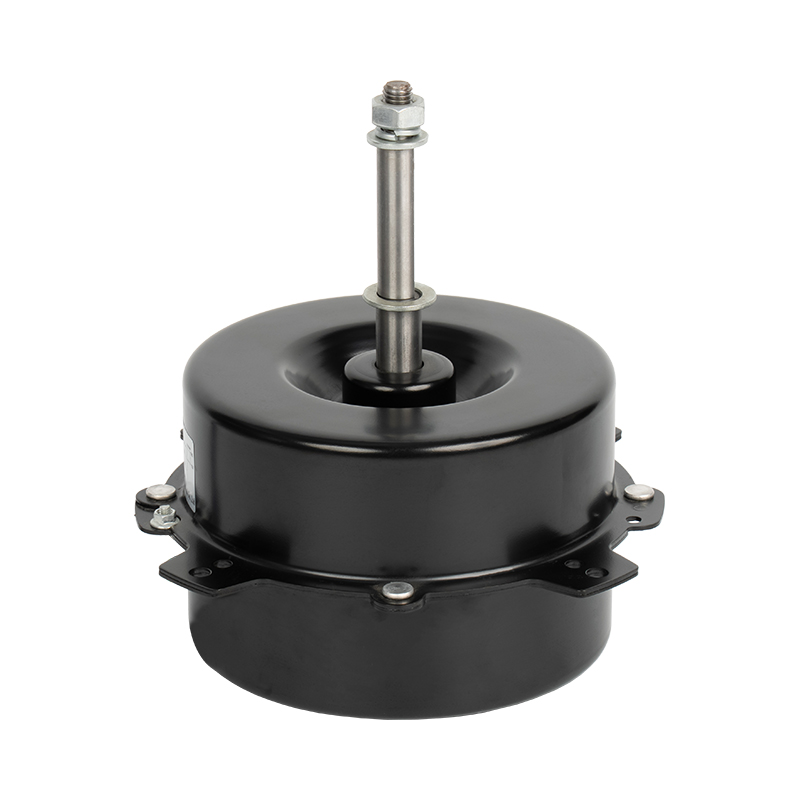
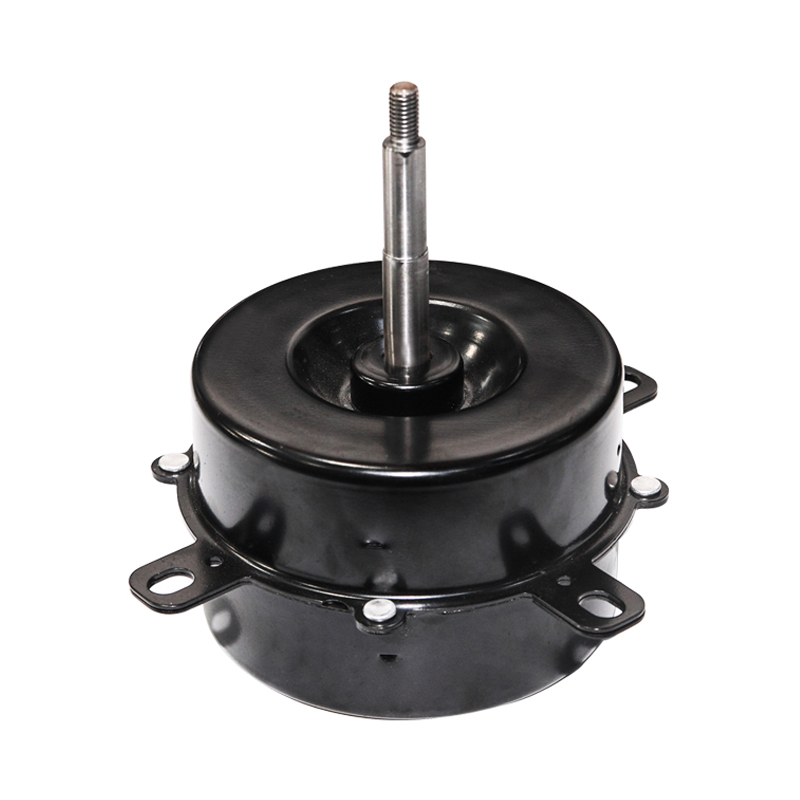
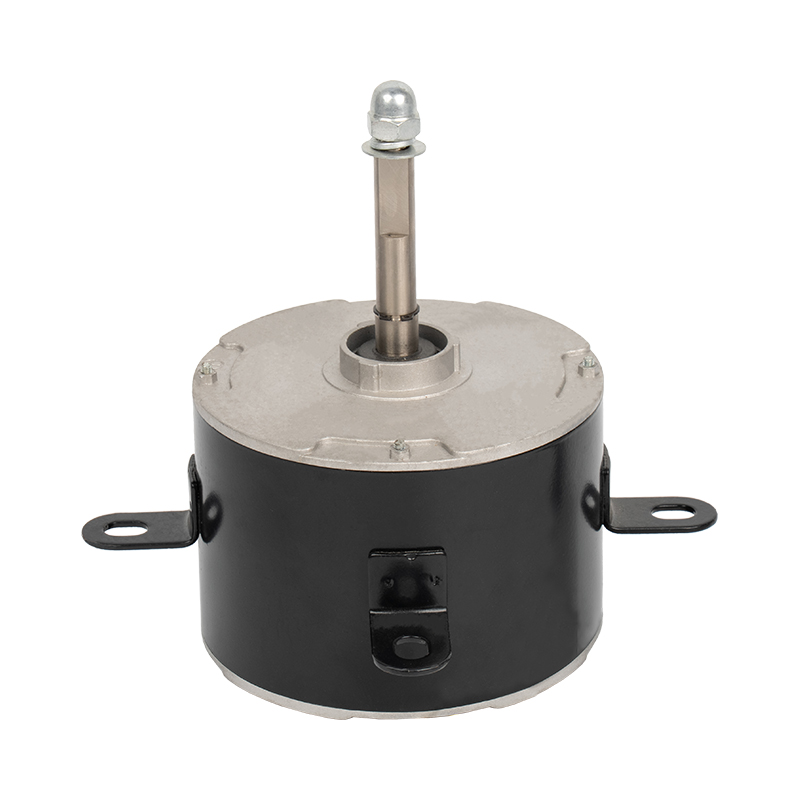
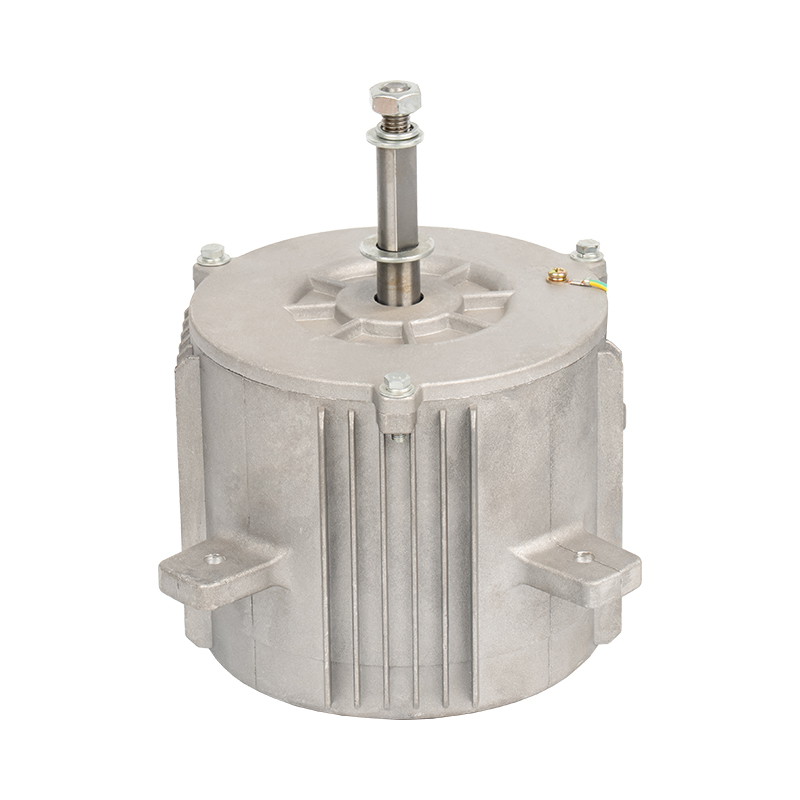
A brushed DC motor is a classic type of drive device that directly converts direct current into mechanical rotation. This type of motor has a simple structure and is widely used, commonly found in household appliances, electric toys, and some small devices in vehicles.
The following is a detailed introduction to brushed DC motors:
1. Core Structure
The internal structure of a brushed DC motor mainly consists of several parts:
Stator (fixed part): Usually permanent magnets attached to the inner wall of the casing, responsible for providing a stable magnetic field.
Rotor (rotating part): A rotating coil winding in the center, where current flows to generate magnetic force.
Brushes: This is its core characteristic. The brushes are usually made of carbon and are in close contact with the rotating commutator.
Commutator: Located on the rotor shaft, it works with the brushes to switch the direction of the current.
2. Working Principle
The working principle of this motor utilizes the magnetic principle of "opposite poles attract, like poles repel":
When current flows through the brushes into the rotor coil, the coil generates a magnetic field.
The magnetic field of the rotor interacts with the magnetic field of the outer stator, generating a thrust that causes the central shaft to rotate.
To ensure the motor rotates continuously in one direction, the commutator automatically changes the direction of the current in the coil every time the rotor rotates a certain angle, ensuring that the thrust is always present.
3. Main Advantages
Simple control: Simply connect it to a DC power source (such as a battery), and it starts rotating. Speed control is also convenient; higher voltage results in faster rotation, and lower voltage results in slower rotation.
High starting torque: This type of motor can generate significant power upon startup, suitable for starting with heavy loads.
Low cost: Due to its simple structure, it is inexpensive to manufacture and easy to repair.
4. Maintenance and Limitations
Due to the physical contact in brushed DC motors, some unavoidable issues arise during use:
Mechanical wear: Because the brushes and commutator are constantly rubbing against each other, the brushes will wear down over time and require regular replacement.
Sparking: Friction and current switching may produce small sparks inside, which requires special attention in flammable or explosive environments. Operating noise: Compared to brushless motors, its friction noise is slightly more noticeable.
Content


 English
English عربى
عربى













 Home
Home  Tel.: +86-13819807486
Tel.: +86-13819807486 Whatsapp:+86 13819807486
Whatsapp:+86 13819807486 E-mail:
E-mail: