The lifespan of a brushed DC motor cannot be generalized, as it's like a car tire – the wear rate depends on how and where you use it.
Here are some key factors affecting its lifespan:
1. Core Loss: The "Lifespan" of the Brushes
This is the most important factor determining how long the motor will last.
Physical wear: The brushes (usually made of carbon) constantly rub against the rotating commutator during operation. Like an eraser, the more you rub, the less is left.
Spark erosion: During rotation, tiny electrical sparks are generated between the brushes and the commutator, which gradually "eats away" at the metal surface. Once the brushes are worn out, the motor can no longer be powered and will stop working.
2. Impact of Working Intensity
Rotation speed: If you make the motor rotate at high speed continuously, friction will increase, generating more heat, and the brushes will wear out very quickly.
Load size: Making the motor pull heavy loads increases the current and strengthens the sparks, accelerating the aging of internal components.
3. Environmental Factors
Dust and impurities: If the environment is dusty, the dust particles entering the motor will act like an abrasive, accelerating the wear of the brushes and bearings.
Heat dissipation: If the motor gets too hot, the internal insulation and lubricant will deteriorate. Maintaining good ventilation can significantly extend its service life.
4. Key "Life-Extending" Measures
A major characteristic of brushed DC motors is that they are usually repairable:
Brush replacement: Many medium and large brushed DC motors allow you to replace only the worn brushes. As long as the replacement is done in time and the core commutator is not damaged, the motor can be "fully restored."
Regular cleaning: Blowing away the accumulated carbon powder (the powder worn off the brushes) prevents internal short circuits and ensures smoother operation.
Content


 English
English عربى
عربى
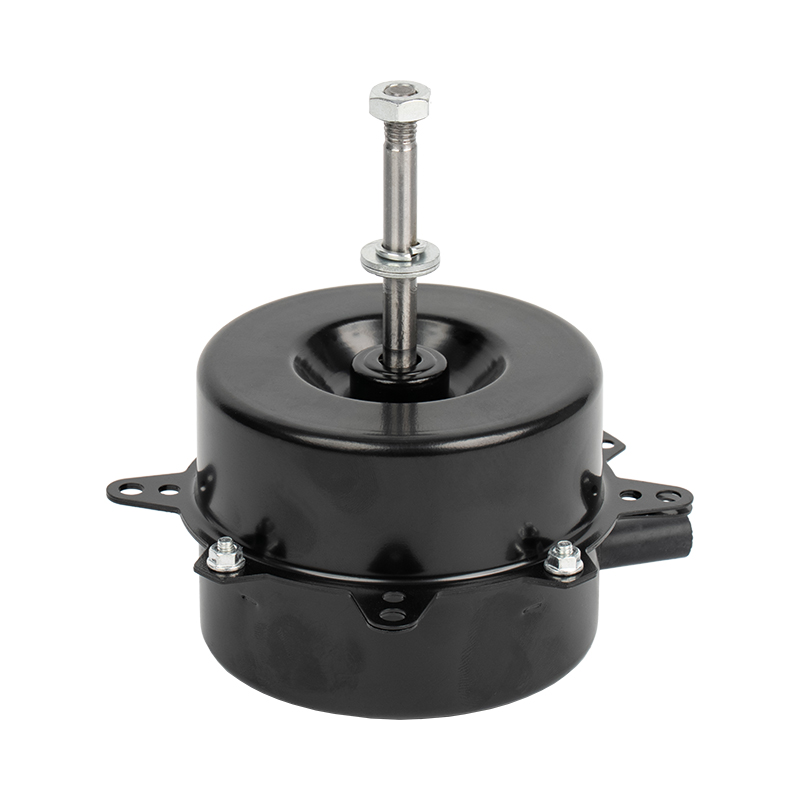
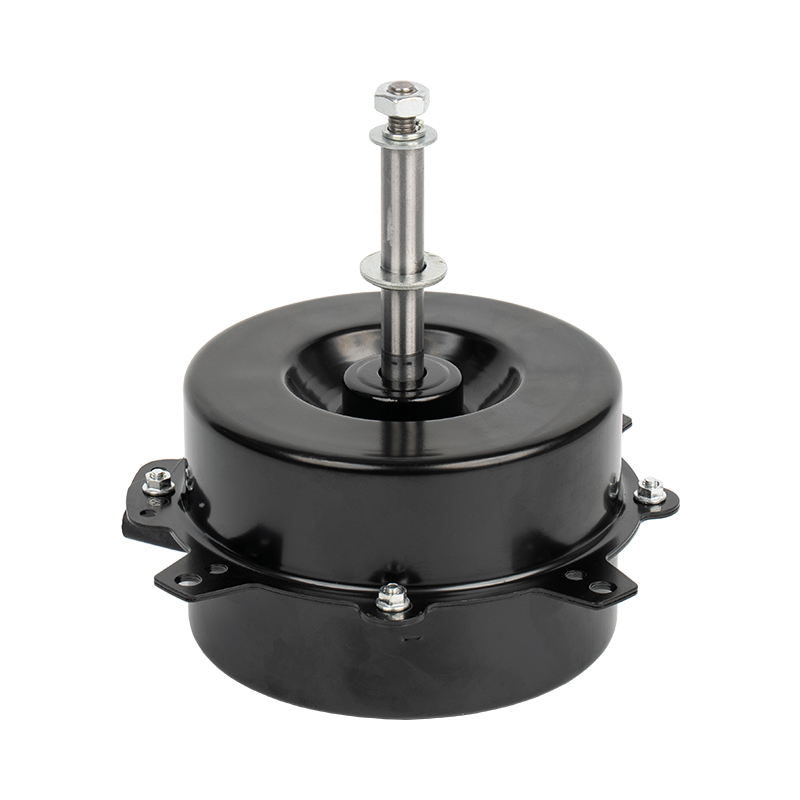
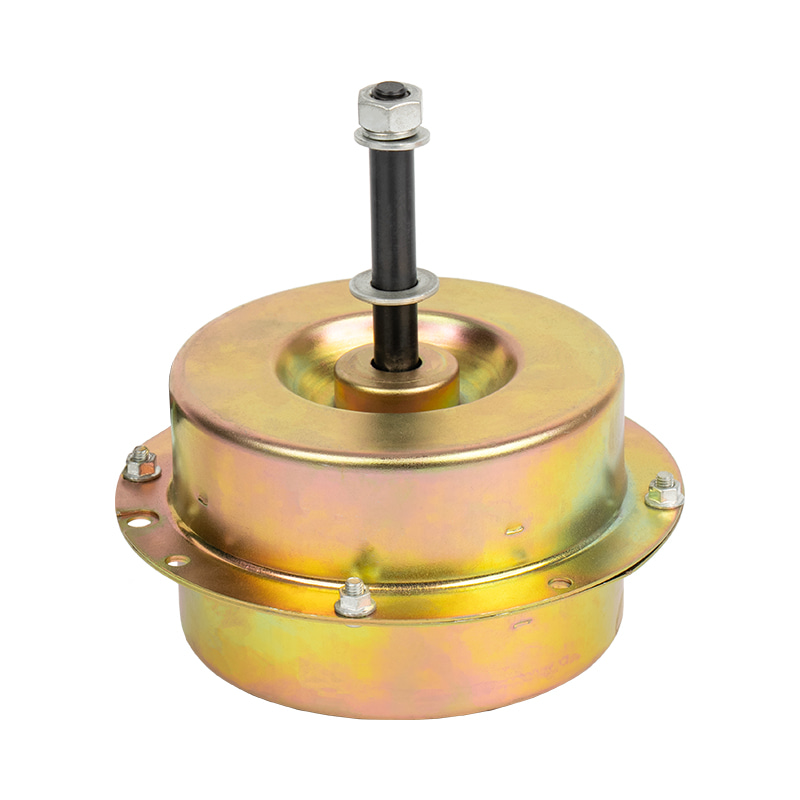
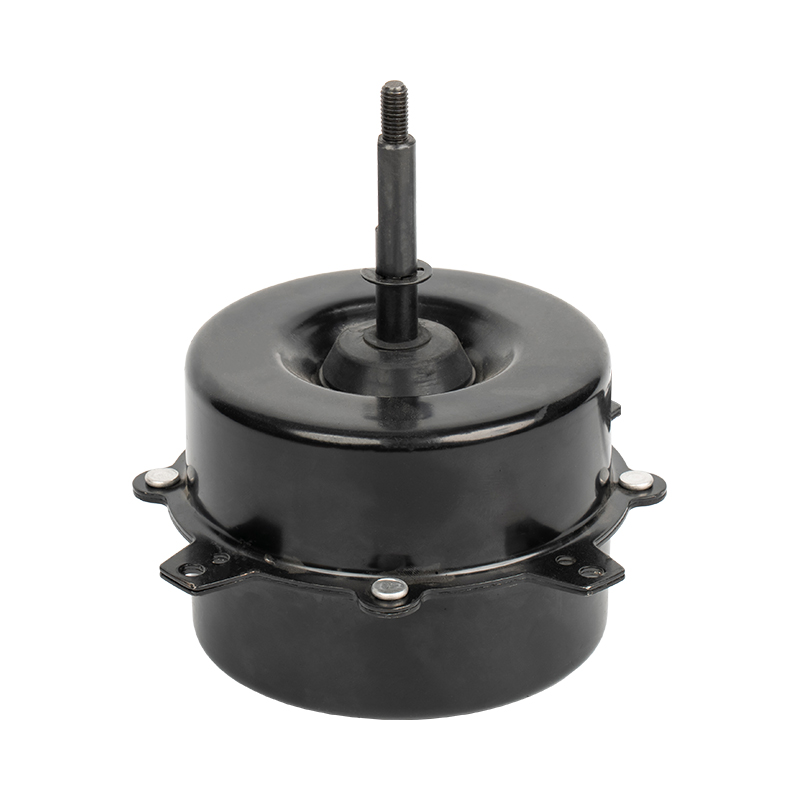













 Home
Home  Tel.: +86-13819807486
Tel.: +86-13819807486 Whatsapp:+86 13819807486
Whatsapp:+86 13819807486 E-mail:
E-mail: